OFDM: Orthogonal frequency-division multiplexing
It is a method of data transmission where a single information stream is split among several closely spaced narrowband subchannel frequencies instead of a single Wideband channel frequency.
It is an efficient modulation format used in modern wireless communication systems including 5G. OFDM combines the benefits of Quadrature Amplitude Modulation (QAM) and Frequency Division Multiplexing (FDM) to produce a high-data-rate communication system.
QAM refers to a variety of specific modulation types:
- BPSK (Binary Phase Shift Keying)
- QPSK (Quadrature Phase Shift Keying)
- 16QAM (16-state QAM)
- 64QAM (64-state QAM), etc.
FDM is simply the idea that multiple communication channels can coexist by designating a slice of frequency spectrum for each channel. A common example of this is FM broadcast radio.
OFDMA: Orthogonal frequency-division multiple access
An access technology that is used between gnodeB and UE for data transmission on wireless/air interface.
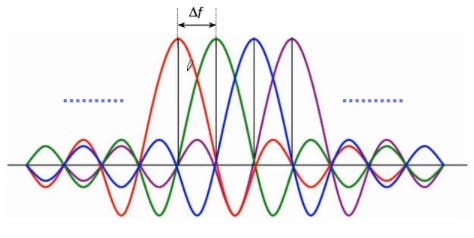 In OFDMA, a frequency band is divided into orthogonal subcarriers(as you can see in above image, here
In OFDMA, a frequency band is divided into orthogonal subcarriers(as you can see in above image, here red,blue,green,pink coloured waves are subcarriers).
Sub-carrier spacing: the spacing between two sub carriers(from centre of one to centre of antoher) represented as Δf.
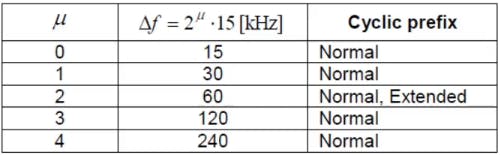
In LTE, Δf is of fixed size i.e 15kHz.
But in 5G, it varies on μ(where μ is flexible numerology).
Flexible Numerology:
also called as scalable carrier spacing.
Now lets understand why we need flexible numerology: As we know that 5G has a wide frequency range so as the frequency increases then we have the problem of intense frequency interference due to effect of :
- Doppler shift
- Phase error
in the oscillator of the receiver what happen that this orthogonality condition may be disturbed. This means that other subscribers don't have their zero value at this point. So as the frequency increases, you have the doppler shift effect that affects the frequency and you have also the phase error due to the difference in phase of the oscillators of the transmitter and the receiver. So even smaller phase error can have a very big impact. So in order to solve this problem because there is no orthogonality then there are inter frequency interference and there are a bit errors and this problem is very aggravated at the high frequencies. So the solution to this problem is to use scalable carrier spacing and the other name of the scalable carrier spacing(flexible numerology).
For example:
Cyclic Prefix:
The guard period between two OFDMA symbols.
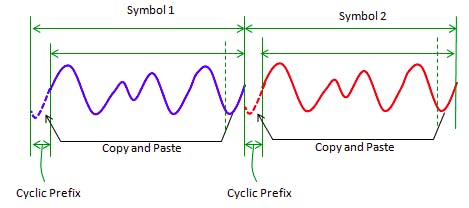 The purpose of this guard period is one symbol does not overlap with other adjacent symbol.
There are two type of cyclic prefixes:
The purpose of this guard period is one symbol does not overlap with other adjacent symbol.
There are two type of cyclic prefixes:
- Normal: The slot is divided into 14 OFDM symbols. Used in the cells which have small area.
- Extended: The slot is divided into 12 OFDM symbols .Used in the cells which have a large area because there will be more bouncing back of the signal from buildings etc.
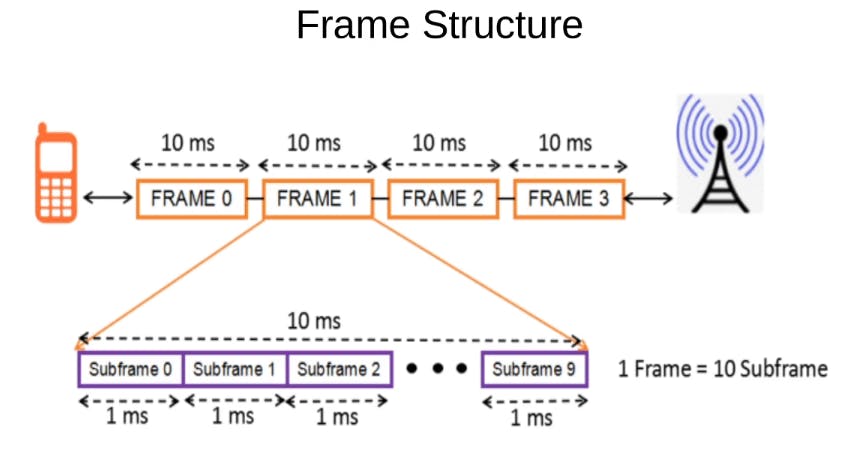
Frame Structures:
In 5G-NR the time is divided into the frames of 10 millisecond and each of these frames is then divided into 10 sub frames and one sub frame has a time of one millisecond.
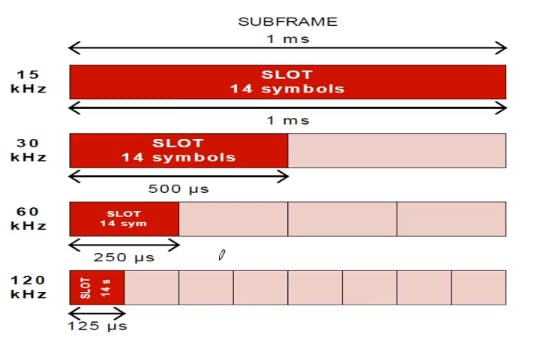
In one subframe with normal cyclic prefix and Δf=15kHz will have one slot of 14 symbols and time take by that one slot will be 1ms.
On moving from 15kHz to 30kHz , slot will be divided into two parts each having 14 symbols and time will be reduced to half i.e 500μs and so on.
Hence number of slots depends on the μ.
 .
.
In short
- Frame -> 10ms
- Subframe --> 1ms
- 1 slot(normal cyclic prefix) --> 14 OFDMA
- 1 slot(extended cyclic prefix) --> 12 OFDMA
