5G System:
When we use any application using our Mobile there are bulk of processes that took place at that time in that network in a very short period of time i.e in
milliseconds. Let's take an example of accessing Google from your Device(UE). When you call Google from your Mobile the process further divided into some subpart:
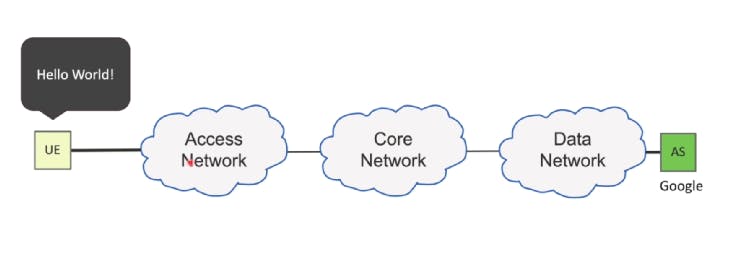 That is when we call google from
That is when we call google from UE --> Access Network --> Core Network --> Data Network --> AS.
Here
- UE - Mobile
- Access Network - 5G-RAN --> Provide Wireless connectivity to the device.
- Core Network - 5G-Core --> Mobility management, Subscription Management, etc.
- Data Network - Internet
- AS - Application Server
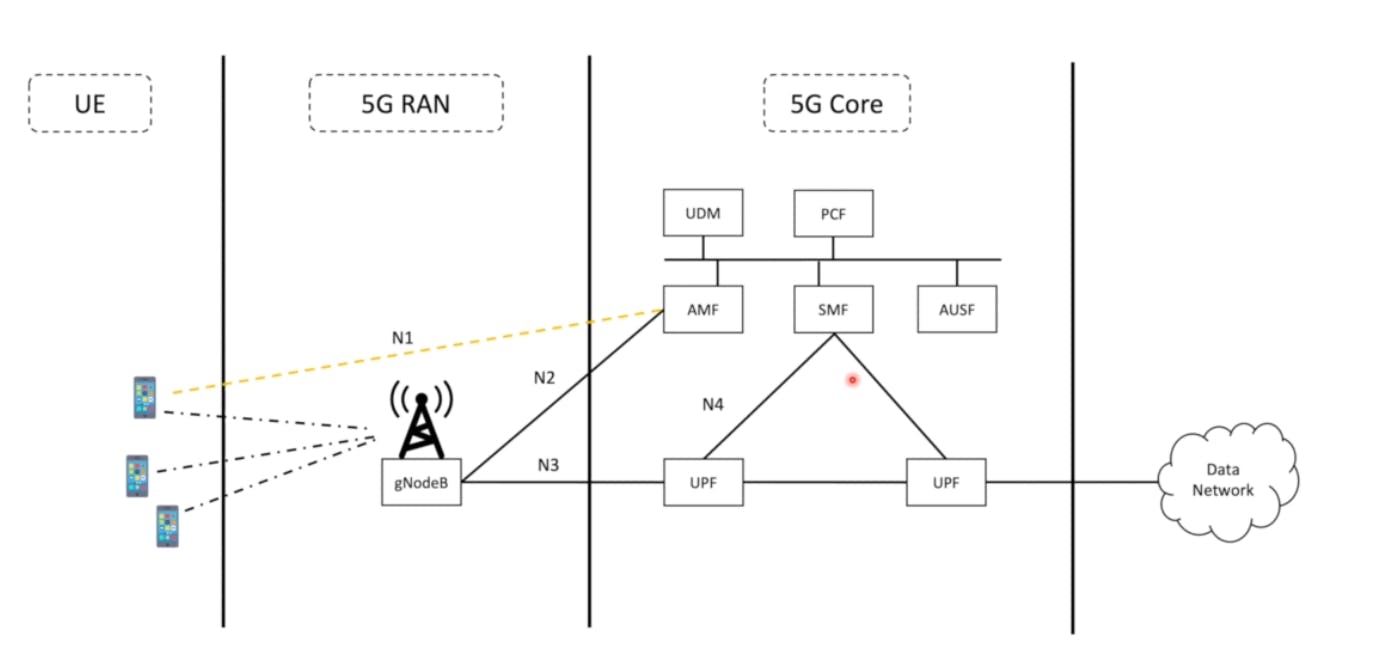
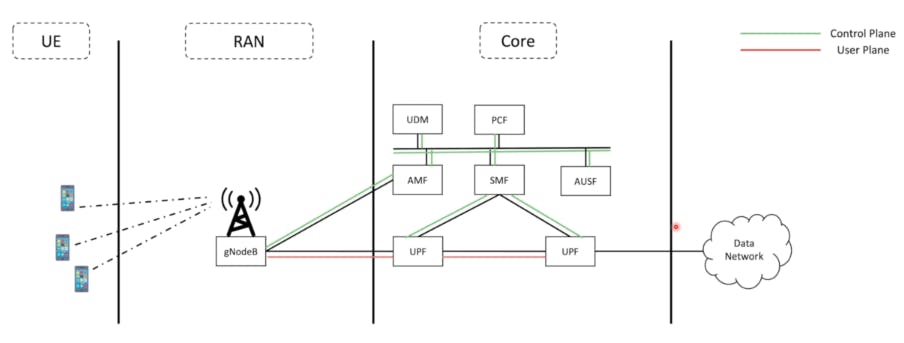
Let's try to understand the following network flow with an architecture:
So, as you can see in this picture the UE is interacting/communication with gNodeB(Radio Tower) and communicates with AMF(5G core) through N1 interface. Similarly, gNodeB is communicating to AMF and UPF through N2 and N3 interfaces. More specifically, gNodeB to AMF --> Control Plane and gNodeB to UPF through User Plane(Data Plane).
- gNodeB has two interfaces :
N2andN3.
Interface: It is just a virtual way of representing the path of communication between devices.
User Plane: (aka data plane, forwarding plane, carrier plane or bearer plane) carries the network user traffic --> data
Network trafficis the amount of data moving across a computer network at any given time. Network traffic, also called data traffic, is broken down into data packets and sent over a network before being reassembled by the receiving device or computer.Control Plane: carries the signaling traffic --> information
- In the Control Plane, the radio resource control (RRC) protocol handles the signalling messages that are exchanged between the base station and the mobile.
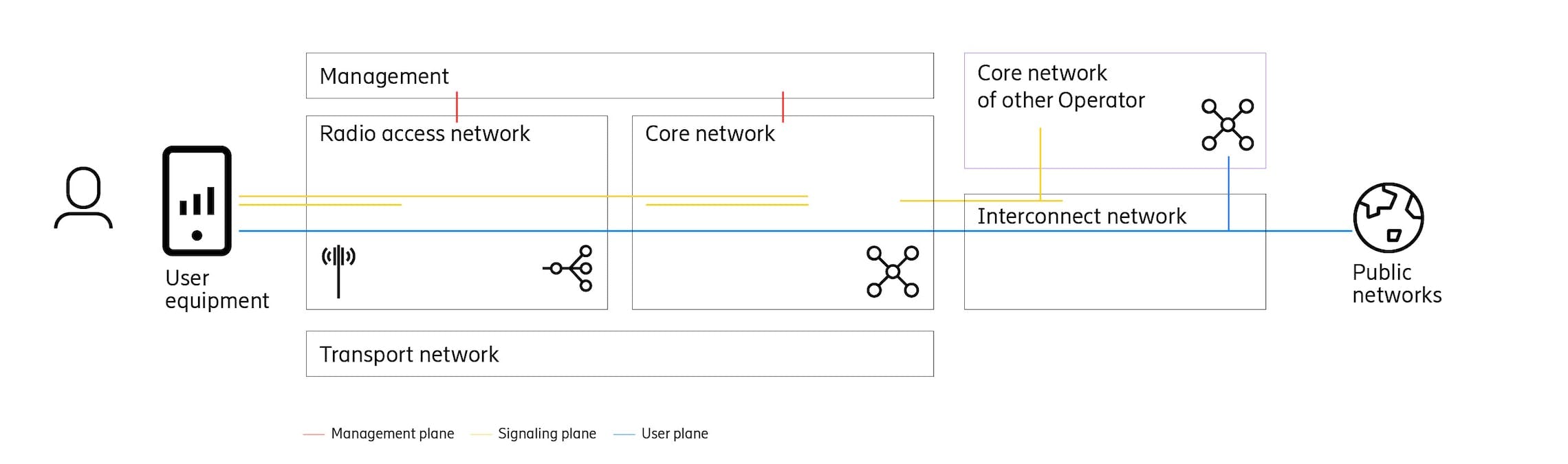
CUPS(Control and User Plane Separation)
Two main Reasons:
- Independent Scaling(for different use case): As we know that there are a lot of devices which are connected to 5G network. So there are two types of devices:
- Massive MTC(Machine Type Communication): Large No. of devices which sends very less data.
Massive MTC <==> Mobile Broadband
- Mobile Broadband: Which sends lot of data. When Massive MTC dominants in the network then there is a need to scale control signal infrastructure and not user signal infrastructure. On the other hand when Mobile broadband dominant which sends a lot of data even if there are fewer devices then there is a need to scale user plane functions and not control signal infrastructure. So, if there is no separation of plane functions then we would end up scaling nodes that handle both control plane and user plane, which is inefficient way of scaling. So, on separation of control and user plane means that we can scale the nodes depending on the exact demand of network. It helps to achieve lower latency and we can optimize the network deployment.
- Flexible Deployments(for different performance): It also give us the freedom to put different functions of 5G-core in the preferred geographical places based on the performance needs.
For example:
 In above image we can see that control plane functions are placed separately than user plane functions.
In above image we can see that control plane functions are placed separately than user plane functions.
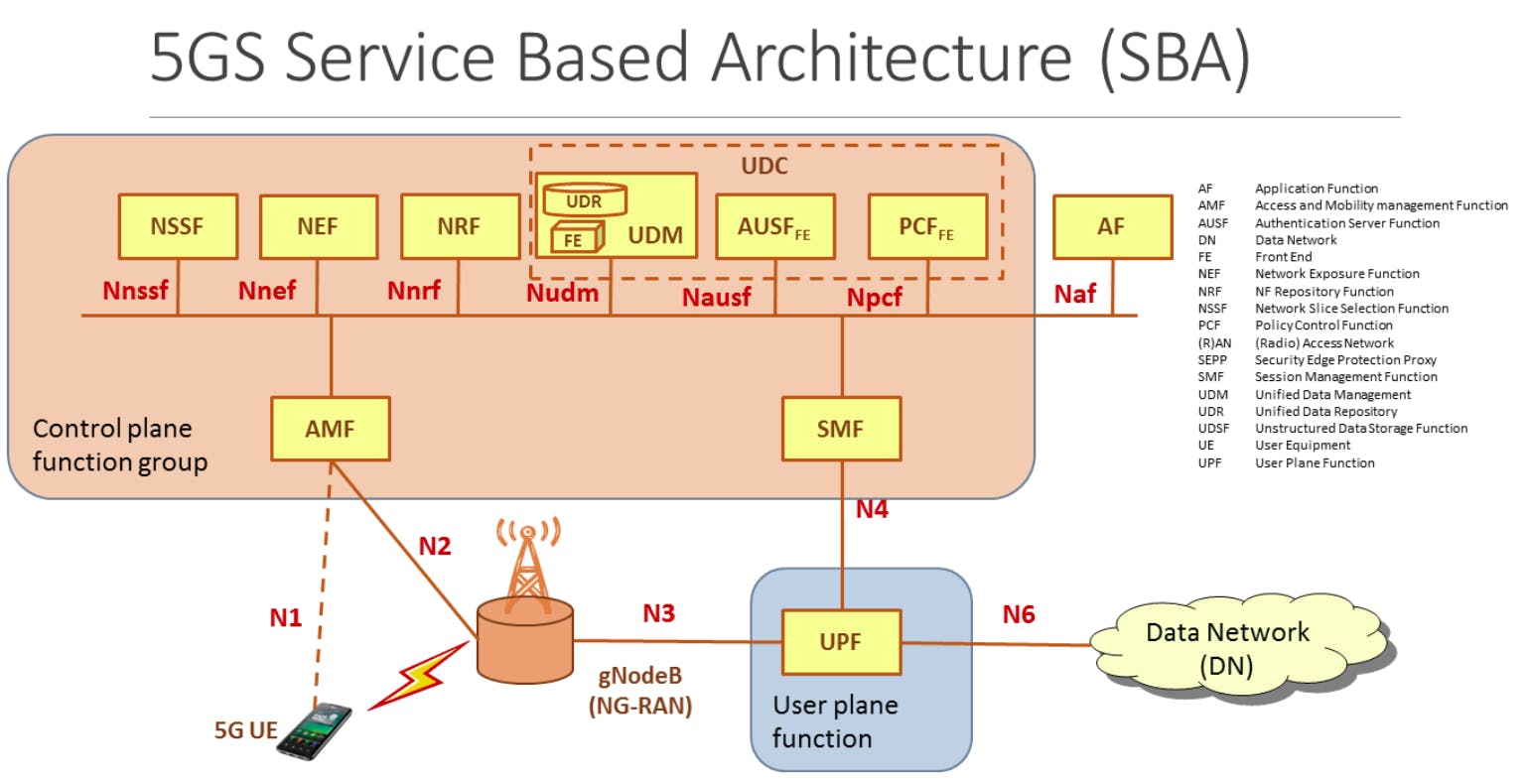
A more enhanced way of representing the above architecture is:
Key Network Functions:
- gNodeB: Establish wireless communication with UE in an efficient manner.
- UPF: Acts as an mobility anchor point and provide interface to the Internet. A good place to enforce policies(ensure that the device doesn't exceed the amount of data that the user has in their subscription. A good point for lawful interception.
- AMF: Tracks the mobility of UE from region to region. Responsible for supporting the devices to move between different radio cells. Forwards messages from UE to other functions like SMF.
- SMF: perform Session management, provide IP address
- AUSF: Authentication functions --> Supports AMF to authenticate the user and get ready to access the internet.
- UDR: Data Repository for all functions that stores the USD(user subscription data)
- UDM: A frontend to USD. It supports AMF in the process of access authorization, registration management for the device, etc.
- PCF: Charging related functions.
- Two type of policy support:
- Session management policies: traffic support
- Non-Session management policies: access and mobility.
- Two type of policy support: