5G Architecture-gNB:
- Radio Transmission/Reception
- Digital Signal Processing(encryption,data compression)
- Process Access Stratum Signaling (between UE and gNB)
- Relay Non-Access Stratum signaling to core (between UE and 5GC)
Radio resource management(which resource blocks to be used by UE, at what power transmission take place, etc..)
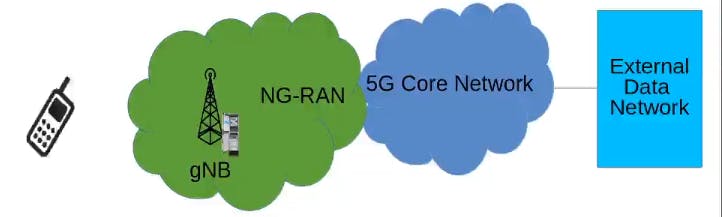
- Communication with core network and nearby base stations (coz there is a link between two gNB known as Xn interface, so when a mobile is moving from coverage area of one gNB to another gNB then in that case when this mobile attaches to that gNB and this porcess is called
handover, so in oder to do this handover there needs to be a signalling between the gNBs over the Xn interfece, so gNB is responsible for handleing that signaling.
PDU Session: Protocol Data Unit
5G is an all IP system i.e. all the services(voice, data, multi-media) take place over IPs packets. In order to prrvide those services, the network needs to establish PDU sessions to the UE and each PDU session may consist of one or more QoS flows. Let say a UE request to 5GC for surfing the browser then in that case it uses QoS flow 1 and at the same time this user is also on voice call then data of voice call passes through QoS flow 2. So QoS flow series depends on the request of the user.
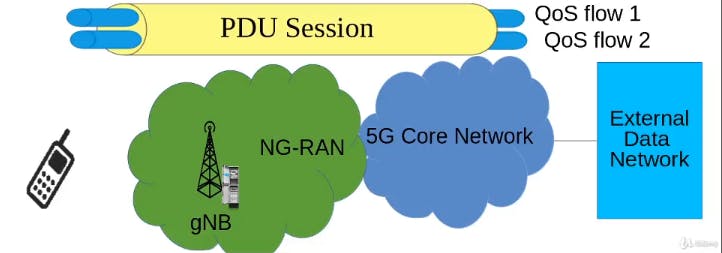
5G provides data connectivity to UE as PDU sessions.
- QoS is characterised by:
- datarate:
- guranteed or non-guranteed
- latency
- priority Because if we compare voice service with the surfing of the internet, the quality of service requiurements for these two services are very different from one another because we cannot allow the delay to supass a certain limit in case of packet flow and of course the priority of voice packet is higher.
- datarate:
So a PDU session contains more that one QoS flows and each flow is identified by a QoS ID.
Also a UE at a time can establisih one PDU session per network slice.
we will cover network slice later on.
Control Plane/User Plane separation:
 Service above (---) lies under user plane and services above (---) lies under control plane.
Service above (---) lies under user plane and services above (---) lies under control plane.
Control Plane Fucntion:
- Authentication(i.e AUSF)
- Connection Management
- QoS Management(i.e SMF)
- Mobility Management(i.e AMF)
User Plane function:
- Data traffic forwarding
Advantage of separation of CP and UP: Scalability
- For example: If the data requirement of the user increases then it is handeled by UP else by CP.
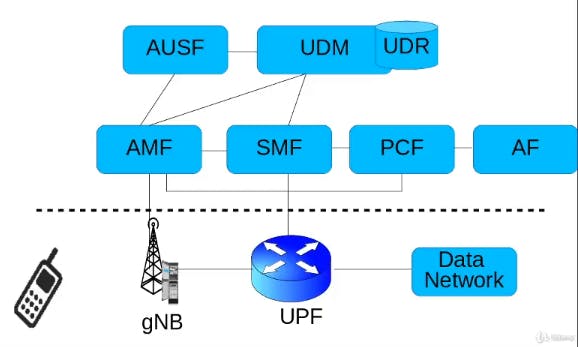
Core Network Architecture
AMF:
The first thing thta a UE does is that it registers itself with the network and the network funcion that is responsible for the registration of the mobile is AMF. If a UE is not in a call or in IDLE mode, in both the cases, the network function with which the UE is directly communicating via gNB is AMF.
It is similar to:
- MME in LTE
- VLR in GSM
Manage UE registration
Initiates Authentication (when UE wants to register with AMF)
Mobility Management
The UE can be in any of the two states either in IDLE i.e if this UE has already registered itself to the network but it is not in the call. In that case the location of this UE is known to the network at the tracking area level.
Tracking Area(TA):
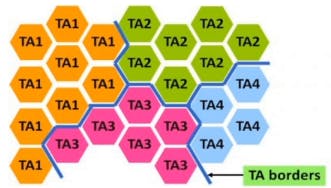
The cells in the 5G network are divided into the tracking areas.
A group of cells have one tracking area number, another group of cells have another tracking area number, so when the UE is in IDLE mode and it moves from one cell having one TA to another cell having different TA then in that case the TA number of this UE needs to be updated in the core network.
And this updation procedure is done by the AMF.
When the UE is in call, then its location is known to the network uptill the cell level. So when a mobile move from one cell to another cell in that case its cell location needs to be updated and this procedure is also handled by AMF.
AUSF:
Authentication Server Function
When UE tries to register itself to a network or it wants to make a call, it needs to be authenticated which will be initated by AMF. In order to perform this authentication we need two more entities i.e UDM and AUSF. So whenever AMF initiates the authentication process, it basically sends the identity to the AUSF and AUSF in turn requests the UDM to generate the authentication vector. This authentication vector is generated by the UDM based upon the secret key that is there with UDM and then this authentication vector is passed on to the AUSF and AUSF then passes this authentication vector to the AMF, now within that authentication vector there is a random number and AMF challenges the UE with that random number by sending it to the UE. After receiving the random number UE generates a authentication response which goes to the AMF and which is then passed on the AUSF and AUSF now checks whether it is a valid authentication response or not and based on that AUSF decides that whether this UE is authenticated or not.
SMF:
Session Management Function
We know that whenever an UE wants to use data services of 5G network, it needs to establish PDU sessions with 5GC. So establishment and management of this PDU session is done by SMF. Also SMF needs to coordinate with the PCF and it is the PCF that decides that under the given network conditions whether this PDU session can be established or not. With what Qos this PDU session is established is also decied by this PCF function. SMF also coordinated with the UPF. It selects the UPF with which the user equipment(UE) established the PDU session. There may be more than one UPF and similarly for the establishment of this PDU sessions SMF actively coordinates or interacts with the UPF and also another very important point is that as a part of the establishment of this PDU session, SMF needs to allocate the IP address/es to the UE. So this allocation is also done by SMF.
Similar to :
- PD-GW Control Plane inLTE.
UPF:
User Plane Function
UPF is a point of contact of data network with 5GC network. And whenever data packet arrives from data network, it is the UPF that decides that where it needs to route those packets. Similarly on the other side , UPF is an anchor for the UE it means that for example this UE has established a PDU session with the UPF, Now if the user is moving it may go from the coverage area of one gNB to another gNB but it would always be anchored with this UPF, i.e it would always have its PDU session established with this UPF, no matter with which gNB this UE is connected.
Also we know that PCF decides that what would be the QoS of this PDU session and this decision is then taken by the SMF and it is then intimated to the UPF. So enforcement of this QoS decision is done by UPF. It is the UPF that implements the QoS for this PDU flow.
Similar to:
- PDN-GW Data Plane in LTE
UDM:
Unified Data Management
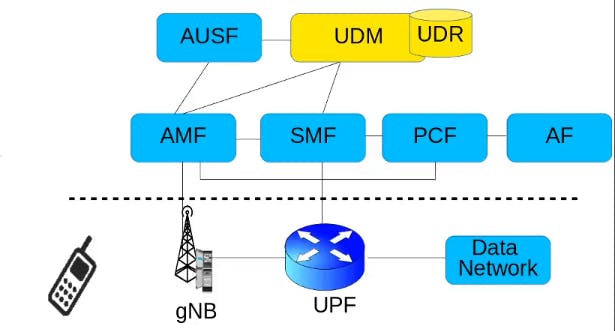 UDM is the centralized database for all the subscribers that are in the there in 5G network. So the proper functioning of UDM is very important. It holds the security keys based upon which the different mobile subscribers are authenticated, i.e whether they can use the network or not. Similarly as the UE moves and it moves from one gNB to another gNB it may go to a gNB which is under the control of AMF. So this UDM keeps track of that in which AMF area which UE is currently located. Similarly UDM holds these subscriber information for all the subscribers in the network like what type of data services a subscriber can use and with what quality of services that he can use these services also which service a user can access and which can't. Also UDM has the information that the user is allowed to room in certain tracking areas or not coz the user can be restricted in from going in cretain tracking areas or certain service ares. Similarly roaming restrictions, that for example a user is coming from a different 5G operator and it wants to use the services of this network. So whether it is allowed to roam in this network or not, this info is also in UDM.
UDM is the centralized database for all the subscribers that are in the there in 5G network. So the proper functioning of UDM is very important. It holds the security keys based upon which the different mobile subscribers are authenticated, i.e whether they can use the network or not. Similarly as the UE moves and it moves from one gNB to another gNB it may go to a gNB which is under the control of AMF. So this UDM keeps track of that in which AMF area which UE is currently located. Similarly UDM holds these subscriber information for all the subscribers in the network like what type of data services a subscriber can use and with what quality of services that he can use these services also which service a user can access and which can't. Also UDM has the information that the user is allowed to room in certain tracking areas or not coz the user can be restricted in from going in cretain tracking areas or certain service ares. Similarly roaming restrictions, that for example a user is coming from a different 5G operator and it wants to use the services of this network. So whether it is allowed to roam in this network or not, this info is also in UDM.
Similar to:
- HSS in LTE
- HLR in GSM
PCF
Policy Charging Function
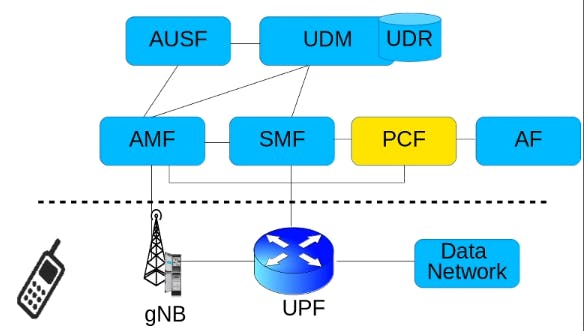
PCF is involved in that dynamic policy decisions based upon network conditions such as congestion, subscriber geo-location etc.. For example: A UE is located in a gNB where it has bad wireless channel conditions and this UE wants to make a call. So this request of a call would reach the PCF through the SMF. Now here PCF can make two decisions:
- One decision is to throttle the data rate of that UE so that it can make a video or it can refuse the call altogether i.e PCF can refuse the call altogether. So in this case the PCF is closely interacting with the session management function(SMF).
- Similarly PCF is also invloved in the management of service areas.
Service area: is the list of allowed and not allowed TA. So if a UE is in TA that is not allowed for this user and if the UE wants to make a call, then PCF can interact with AMF and it can refuse that call altogether. So PCF can interact with AMF, SMF and also with AF. When UE makes a call and uses the services of a 5G network, how that user is charged/billed, is also decided by PCF which may take into account the factors like what QoS is being offered to a user.
Similar to:
- PCRF in LTE
NFV and Slicing:
NFV: Network Function Virtualization
• Problem with traditional mobile networks
- Network nodes implemented as special-purpose hardware
- the hardware is expensive to procure, install and maintain;
- the hardware eventually needs to be replaced
- difficult for new hardware vendors to enter the market;
- difficult to upgrade the network to support new use cases e.g., machine type communication
So solution of these problems is using NFV.
• NFV Approach
- network's functionalities is implemented in software,
- which runs on COTS (Commercial Off The Shelf) hardware such as servers, storage and switches (i.e which is easily available).
• NFV brings several advantages:
- the costs of both hardware and software reduces
- easier for new vendors to enter the market;
- far easier to upgrade the network by simply upgrading the software.
NVF Architecture by ETSI:
• Virtual Network Function: Software implementation of a network function NFV Infrastructure: Physical hardware resources, such as computing, storage and networking. The resources are abstracted and logically partitioned by means of a virtualization layer • NFV Management and Orchestration encom asses the mana ement of the Physical resources, virtual resources and VNF
![5G-NR[core]](https://cdn.hashnode.com/res/hashnode/image/stock/unsplash/M2VtwQSkQFs/upload/72aab3a35610c165d65134b332f1fabf.jpeg?w=1600&h=840&fit=crop&crop=entropy&auto=compress,format&format=webp)
